J.J. Lally & Co., Oriental Art / New York City, New York
MenuPast Exhibition
Ancient Chinese Bronzes
March 19 - April 9, 2011
25.
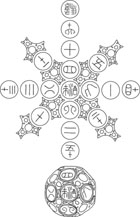
A RARE GOLD- AND SILVER-INLAID BRONZE DIE
Han Dynasty (206 B.C. – A.D. 220)
of almost spherical form, with eighteen flat sides of circular outline each inlaid with a single Chinese character in seal script, including the characters jiu lai (“wine comes to you”) inlaid in silver and jiao possibly meaning “leader” or “win”) inlaid in gold, filling the small medallions at the two opposite pole positions and the numerals 1-16 in silver within gold-edged medallions symmetrically arranged over the surface, further embellished with turquoise, agate and rock crystal inlays surrounded by gold and silver cloud scroll motifs filling the interstices between the faces, the exposed bronze with reddish-brown patination and traces of malachite green corrosion from burial.
Width 1 3⁄8 inches (3.5 cm)
Exhibited
Asian Games: The Art of Contest
Asia Society Museum, New York, October 14, 2004 – January 16, 2005
Freer and Sackler Galleries, Washington D.C., February 26 – May 15, 2005
Middlebury College Museum of Art, Vermont, September 17 – December 11, 2005
Published
Mackenzie and Finkel (eds.). Asian Games: The Art of Contest, New York, 2004, p. 43, no. 2:8 a-b, and on the back cover
A similarly decorated eighteen-sided bronze die inlaid with gold, silver, turquoise, agate, and rock crystal, unearthed in 1968 from the tomb of princess Dou Wan at Mancheng in Hebei province, is illustrated in Mancheng Han mu fajue baogao (Excavation of the Han Tombs at Man-ch’eng), Vol.s I-II, Beijing, 1980, as a line drawing on p. 274 in Vol. I and as pl. CLXXXVI, no. 2 in Vol. II. The Mancheng die was unearthed together with a set of 40 bronze coins cast with 20 rhymes and numbers 1 to 20, possibly made for a drinking game.
Similarly inscribed wood and lacquered die of this form, excavated in 1973 from the Western Han tomb in Fenghuangshan, Jiangling county, Hubei province, are illustrated in the excavation report in Wenwu, 1974, No. 6, p. 59, no. 37; and another wood die excavated in 1973 from a Han dynasty tomb at Mawangdui in Changsha, Hunan province, together with a lacquered wood liubo game set, is illustrated in the excavation report in Changsha Mawangdui er, san hao Han mu (Tombs 2 and 3 from the Han Dynasty at Mawangdui, Changsha: Report on Excavation), Vol. I, Beijing, 2004, col. pl. XXXVI, no. 3.
This complex multifaceted piece is an example of the earliest known form of Chinese die. In a chapter entitled “Liubo: The Five-Hundred-Year Craze” in Asian Games: The Art of Contest, New York, 2004, pp. 113-125, Mackenzie discusses the possible use of this type of die for the board game liubo. In the caption below the illustration of this particular die, op. cit. p. 43, however, he notes that the characters jiu lai indicate that it might have been used for a drinking game.
漢 錯金銀鑲嵌銅骰
寬 3.5 厘米